Trending News
News
News
A Billion-Year-Old Protein Keeps Genomes From Falling Apart
Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory found that Dicer, an ancient RNA-cutting protein shared by humans and yeast, prevents DNA damage by pausing genetic processes that collide during transcription and replication.
News
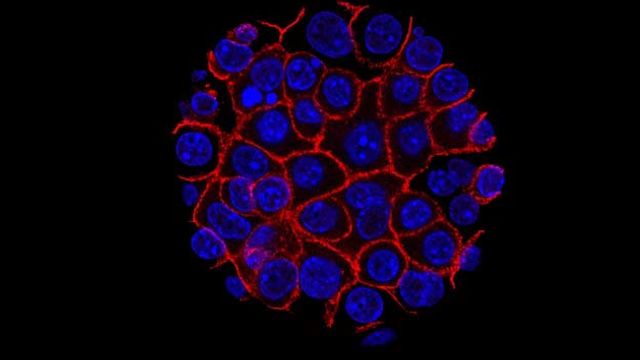
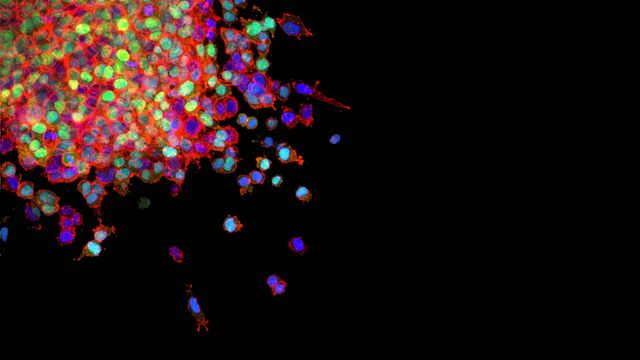
Bioengineered Models Offer Insight Into Early Cancer
Scientific review discusses how new advances in 3D bioprinting, organoids, organs on-a-chip aid in the fight against cancer.
News
New Method Models Chromosomal Abnormalities in Egg Cells
Yale researchers have created a new method for simulating “aging-like” chromosome errors in mouse eggs to better understand female reproductive lifespan.

News
Nutrient Found in Meat and Legumes Enhances Mitochondrial Energy Production
Discover how leucine – an amino acid found in meat, dairy and legumes – increases cellular energy, opening new possibilities for treating metabolic diseases.
News
Nicheformer Reconstructs Tissue Architecture Lost in Cell Sequencing
A new AI model called Nicheformer restores spatial context to single-cell data, showing how cells organize within tissues. Developed by Helmholtz Munich and TUM, the model bridges single-cell and spatial transcriptomics.

News
Immune-Compatible Kidney Organoids Advance Regenerative Therapies
A new bioengineering platform enables the large-scale production of human kidney organoids that can be perfused within pig kidneys, maintaining viability and function without immune rejection.
News
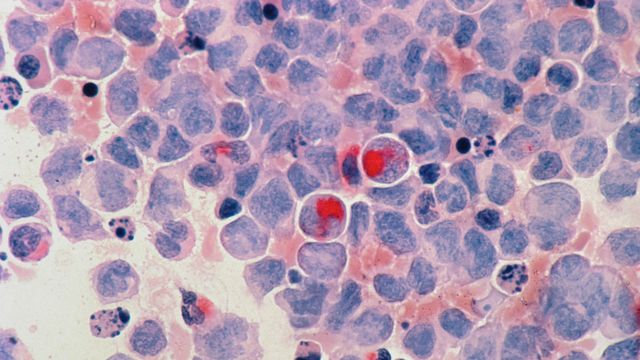
Cell Death Molecular Switch Identified for the First Time
In the fight against disease, programmed cell death, also known as apoptosis, is a key protective function of the body. A research team has now successfully identified a new molecular switch in this process and elucidated its mechanism of action.

News
Beyond Altitude Sickness: How Low Oxygen Can Rewire Your Immune System
Researchers found that brief hypoxia, experienced at altitude or during illness, reprograms bone marrow progenitors, creating neutrophils less effective at fighting bacteria. This epigenetic “memory” persisted for months in climbers after descent.
News
Antiviral Approach Uses Decoys To Block Lethal Viruses
Washington University researchers discovered how yellow fever and tick-borne encephalitis viruses enter human cells and created decoy molecules that block infection, paving the way for new antiviral therapies.
Advertisement